Spontaneous Facial Expressions Are Different from Posed Facial Expressions: Morphological Properties and Dynamic Sequences
Abstract
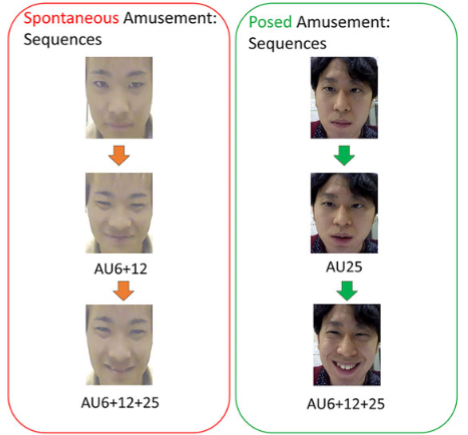
The correspondence between facial expressions and emotions has been widely examined in psychology. However, studies have yet to record spontaneous facial expressions under well-controlled circumstances, thus the characteristics of these expressions remain unclear. Therefore, we compared the morphological and dynamic properties of spontaneous and posed facial expressions related to four different emotions: surprise, amusement, disgust, and sadness. First, we secretly recorded participants’ spontaneous facial expressions as they watched films chosen to elicit these four target emotions. We then recorded posed facial expressions of participants when asked to intentionally express each emotion. Subsequently, we conducted detailed analysis of both the spontaneous and posed expressions by using the Facial Action Coding System (FACS). We found different dynamic sequences between spontaneous and posed expressions for surprise and amusement. Moreover, we confirmed specific morphological aspects for disgust (the prevailing expressions of which encompassed other emotions) and posed negative emotions. This study provides new evidence of the characteristics for genuinely spontaneous and posed facial expressions corresponding to these emotions.